在理解了Server,Service和Executor后,我们可以进入Request处理环节了。我们知道客户端是可以发起多个请求的,Tomcat也是可以支持多个webapp的,有多个上下文,且一个webapp中可以有多个Servlet...等等,那么Tomcat是如何设计组件来支撑请求处理的呢?本节文将介绍Tomcat的Container设计。@anarkh
- Tomcat - Request请求处理: Container设计
- 内容引入
- 理解思路
- Container的设计
- Container的层次结构方法
- Container事件监听相关方法
- Container功能支撑方法
- Container基本实现:ContainerBase
- Logger
- Cluster
- Realm
- name等属性
- child相关
- Lifecycle的模板方法
内容引入
这里一定把握住我们上下文之间的衔接,这是我们整个系列理解Tomcat的主线。@anarkh
- 到目前我们研究到了哪里?
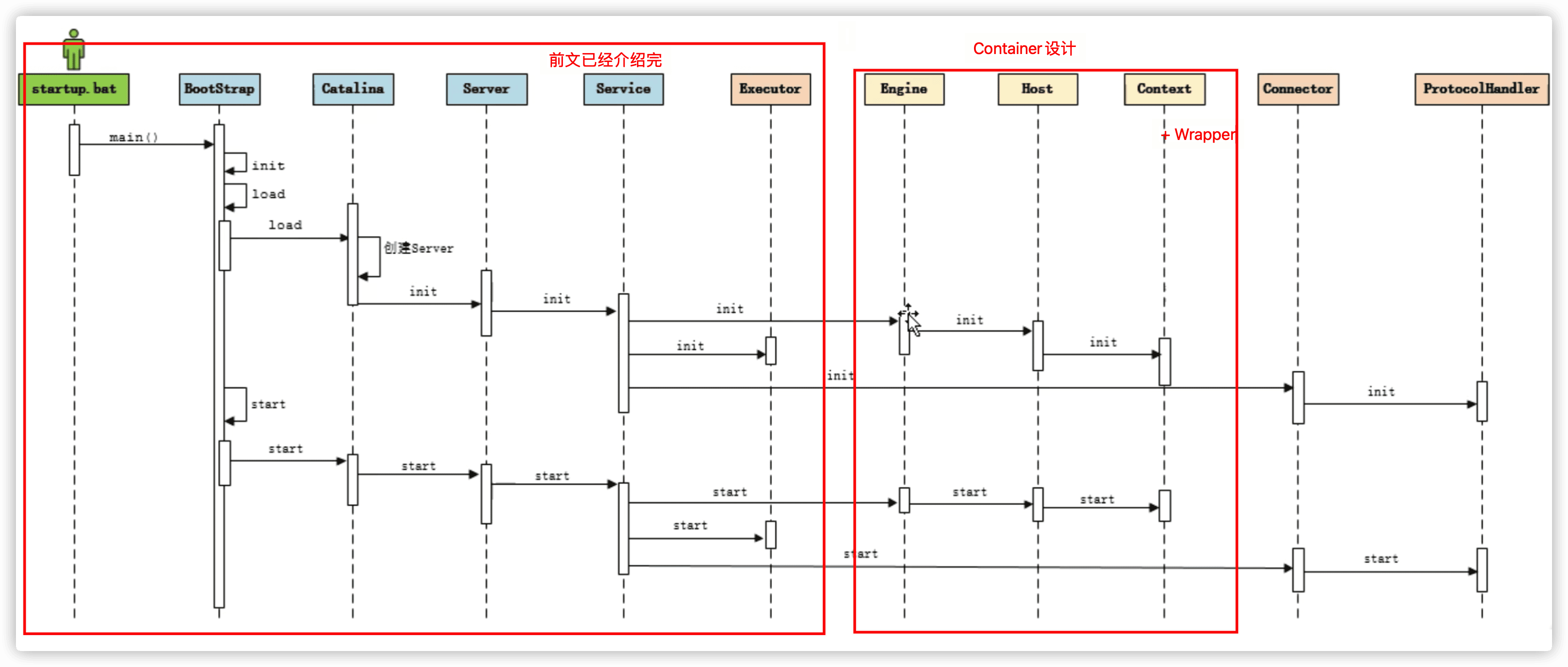
理解思路
- 为什么我们说上面的是Container呢?我们看下几个Container之间的关系 :
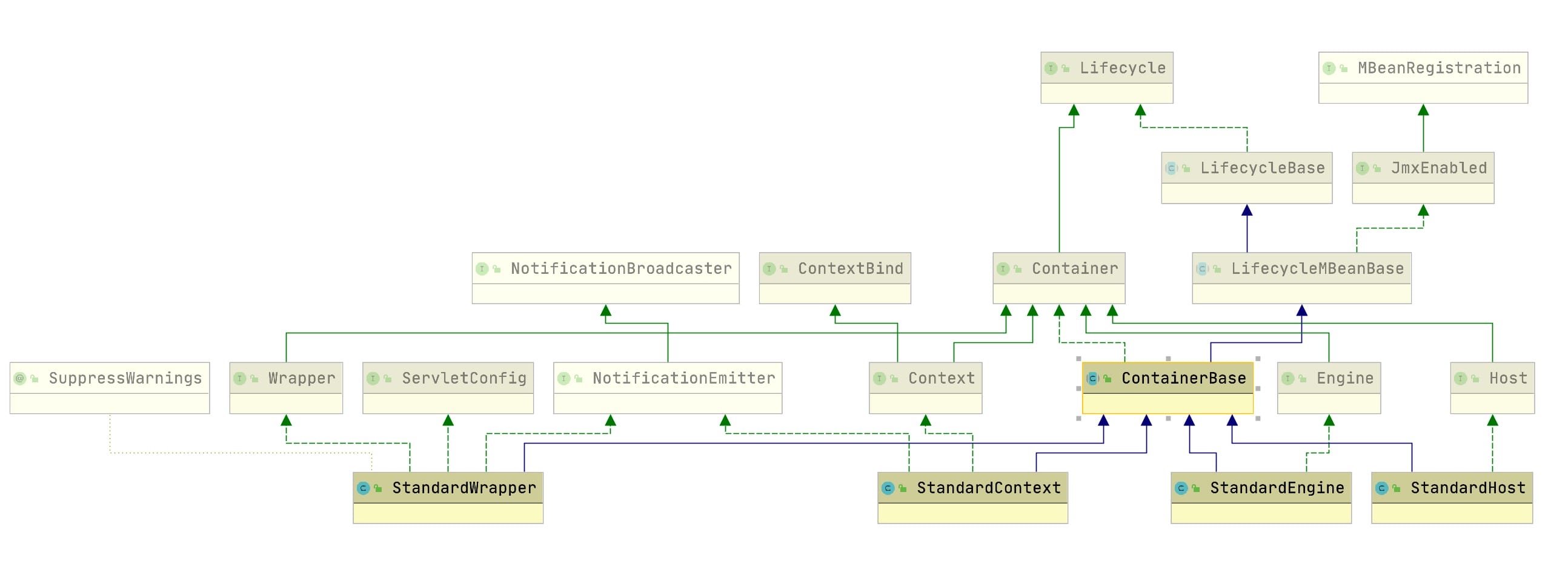
从上图上,我们也可以看出Container顶层也是基于Lifecycle的组件设计的。
- 在设计Container组件层次组件时,上述4个组件分别做什么的呢?为什么要四种组件呢?
如下是Container接口类的相关注释
* <li><b>Engine</b> - Representation of the entire Catalina servlet engine,
* most likely containing one or more subcontainers that are either Host
* or Context implementations, or other custom groups.
* <li><b>Host</b> - Representation of a virtual host containing a number
* of Contexts.
* <li><b>Context</b> - Representation of a single ServletContext, which will
* typically contain one or more Wrappers for the supported servlets.
* <li><b>Wrapper</b> - Representation of an individual servlet definition
* (which may support multiple servlet instances if the servlet itself
* implements SingleThreadModel).
* </ul>Engine - 表示整个catalina的servlet引擎,多数情况下包含一个或多个 子容器,这些子容器要么是Host,要么是Context实现,或者是其他自定义组。
Host - 表示包含多个Context的虚拟主机的。
Context — 表示一个ServletContext,表示一个webapp,它通常包含一个或多个wrapper。
Wrapper - 表示一个servlet定义的(如果servlet本身实现了SingleThreadModel,则可能支持多个servlet实例)。
- 结合整体的框架图中上述组件部分,我们看下包含了什么 ?
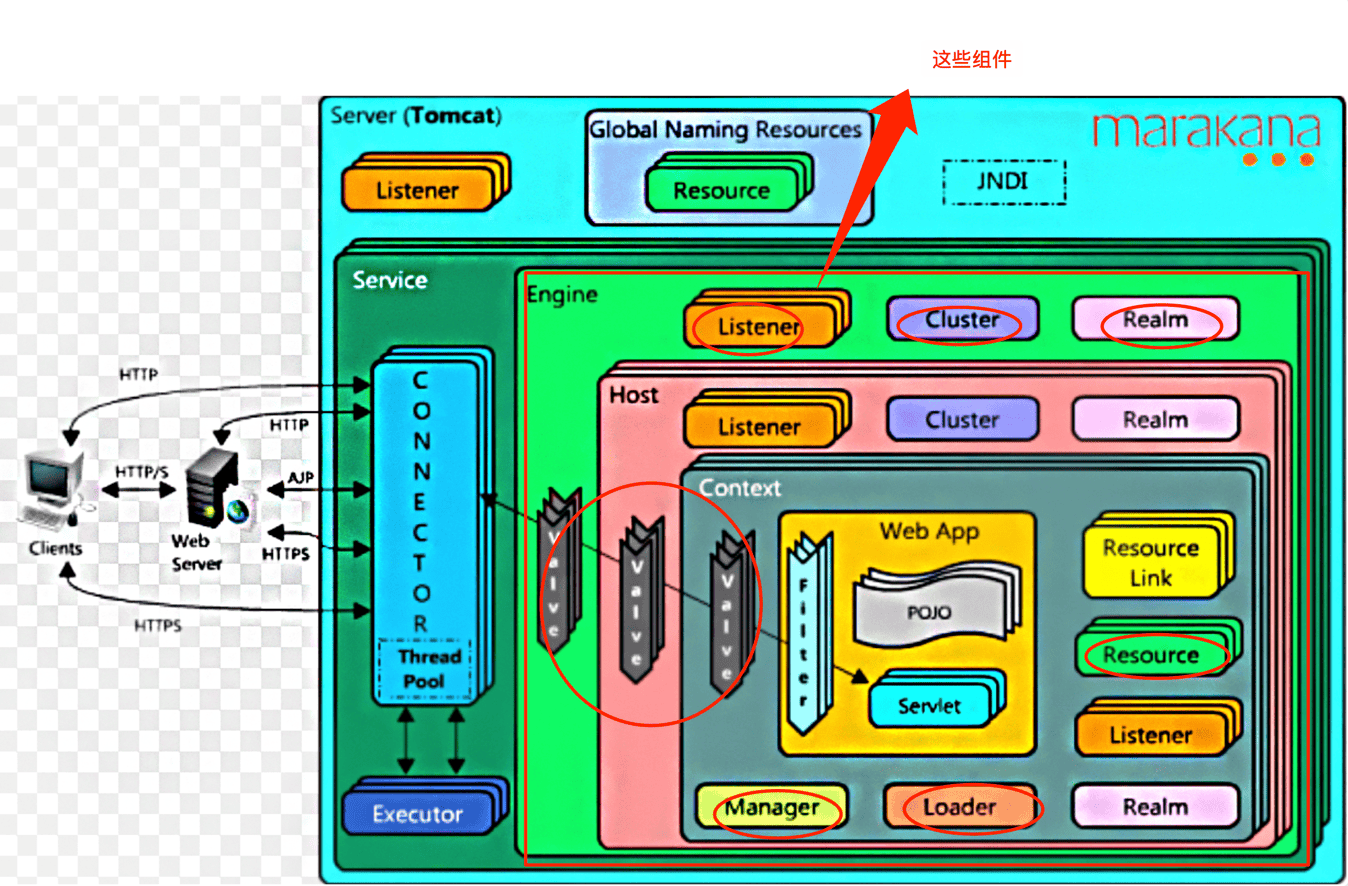
很明显,除了四个组件的嵌套关系,Container中还包含了Realm,Cluster,Listeners, Pipleline等支持组件。
这一点,还可以通过相关注释可以看出:
**Loader** - Class loader to use for integrating new Java classes for this Container into the JVM in which Catalina is running.
**Logger** - Implementation of the log() method signatures of the ServletContext interface.
**Manager** - Manager for the pool of Sessions associated with this Container.
**Realm** - Read-only interface to a security domain, for authenticating user identities and their corresponding roles.
**Resources** - JNDI directory context enabling access to static resources, enabling custom linkages to existing server components when Catalina is embedded in a larger server.Container的设计
这container应该包含哪些接口呢?如果你看源代码它包含二十多个接口,这里理解的时候一定要分组去理解。
Container的层次结构方法
查找父容器的方法:
public Container getParent();
public void setParent(Container container);由于Engine显然上层是Service,所以里面加了一个getService的方法
public static Service getService(Container container) {
while (container != null && !(container instanceof Engine)) {
container = container.getParent();
}
if (container == null) {
return null;
}
return ((Engine) container).getService();
}类比树接口,有Parent方法,那肯定也child方法:
public void addChild(Container child);
public Container[] findChildren();
public void removeChild(Container child);Container事件监听相关方法
前文我们也分析过Tomcat的事件监听机制,Container也是一样, 比如如下的ContainerListener
public void addContainerListener(ContainerListener listener);
public ContainerListener[] findContainerListeners();
public void removeContainerListener(ContainerListener listener);除了Container级别的,和前文我们理解的一样,还有属性相关的Listener, 显然就增删属性的监听方法
public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener);
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener);最后显然还有事件的触发方法
public void fireContainerEvent(String type, Object data);Container功能支撑方法
前面我们知道,Loader, Logger, Manager, Realm, Resources等支撑功能。这里简单看下接口定义,相关基本实现看下节ContainerBase的实现。
- Loader
public ClassLoader getParentClassLoader();
public void setParentClassLoader(ClassLoader parent);- Logger
public Log getLogger();
public String getLogName();- Manager
体现在我们之前分析的JMX管理
public ObjectName getObjectName();
public String getDomain();
public String getMBeanKeyProperties();
public int getStartStopThreads();- Realm
public Realm getRealm();
public void setRealm(Realm realm);- Cluster
public Cluster getCluster();
public void setCluster(Cluster cluster);- 其它
public String getName();
public void setName(String name);
public void setStartStopThreads(int startStopThreads);
public File getCatalinaBase();
public File getCatalinaHome();Container基本实现:ContainerBase
就讲讲几个比较核心的
Logger
日志记录器,比较简单,直接看代码
@Override
public Log getLogger() {
if (logger != null)
return logger;
logger = LogFactory.getLog(getLogName());
return logger;
}
@Override
public String getLogName() {
if (logName != null) {
return logName;
}
String loggerName = null;
Container current = this;
while (current != null) {
String name = current.getName();
if ((name == null) || (name.equals(""))) {
name = "/";
} else if (name.startsWith("##")) {
name = "/" + name;
}
loggerName = "[" + name + "]"
+ ((loggerName != null) ? ("." + loggerName) : "");
current = current.getParent();
}
logName = ContainerBase.class.getName() + "." + loggerName;
return logName;
}Cluster
getCluster:读锁,获取子类的cluster,如果没有则返回父类的cluster;getClusterInternal: 读锁,获取子类的clustersetCluster: 写锁,设置container的cluster;由于cluster具备生命周期,所以需要对停止旧的cluster,启动新的cluster;设置成功后,再触发cluster变更事件。
protected Cluster cluster = null;
private final ReadWriteLock clusterLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
protected Container parent = null;
@Override
public Cluster getCluster() {
Lock readLock = clusterLock.readLock();
readLock.lock();
try {
if (cluster != null)
return cluster;
if (parent != null)
return parent.getCluster();
return null;
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
protected Cluster getClusterInternal() {
Lock readLock = clusterLock.readLock();
readLock.lock();
try {
return cluster;
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void setCluster(Cluster cluster) {
Cluster oldCluster = null;
Lock writeLock = clusterLock.writeLock();
writeLock.lock();
try {
oldCluster = this.cluster;
if (oldCluster == cluster)
return;
this.cluster = cluster;
if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldCluster != null) &&
(oldCluster instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) oldCluster).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.cluster.stop"), e);
}
}
if (cluster != null)
cluster.setContainer(this);
if (getState().isAvailable() && (cluster != null) &&
(cluster instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.cluster.start"), e);
}
}
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
support.firePropertyChange("cluster", oldCluster, cluster);
}Realm
Realm和上面的Cluster方法基本一致。
@Override
public Realm getRealm() {
Lock l = realmLock.readLock();
l.lock();
try {
if (realm != null)
return realm;
if (parent != null)
return parent.getRealm();
return null;
} finally {
l.unlock();
}
}
protected Realm getRealmInternal() {
Lock l = realmLock.readLock();
l.lock();
try {
return realm;
} finally {
l.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void setRealm(Realm realm) {
Lock l = realmLock.writeLock();
l.lock();
try {
Realm oldRealm = this.realm;
if (oldRealm == realm)
return;
this.realm = realm;
if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldRealm != null) &&
(oldRealm instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) oldRealm).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.realm.stop"), e);
}
}
if (realm != null)
realm.setContainer(this);
if (getState().isAvailable() && (realm != null) &&
(realm instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.realm.start"), e);
}
}
support.firePropertyChange("realm", oldRealm, this.realm);
} finally {
l.unlock();
}
}name等属性
此类属性改变时触发属性变更事件,比如name是容器的名字,name变更会触发name变更事件。
protected String name = null;
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public void setName(String name) {
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("containerBase.nullName"));
}
String oldName = this.name;
this.name = name;
support.firePropertyChange("name", oldName, this.name);
}child相关
添加子容器
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> dp =
new PrivilegedAddChild(child);
AccessController.doPrivileged(dp);
} else {
addChildInternal(child);
}
}
private void addChildInternal(Container child) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Add child " + child + " " + this);
}
synchronized(children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
sm.getString("containerBase.child.notUnique", child.getName()));
child.setParent(this);
children.put(child.getName(), child);
}
fireContainerEvent(ADD_CHILD_EVENT, child);
try {
if ((getState().isAvailable() ||
LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(getState())) &&
startChildren) {
child.start();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("containerBase.child.start"), e);
}
}查找子容器
@Override
public Container findChild(String name) {
if (name == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (children) {
return children.get(name);
}
}
@Override
public Container[] findChildren() {
synchronized (children) {
Container results[] = new Container[children.size()];
return children.values().toArray(results);
}
}- 删除子容器
子容器有生命周期,所以应该是先停止,然后销毁(distroy), 再触发删除事件,最后将children中子容器删除。
@Override
public void removeChild(Container child) {
if (child == null) {
return;
}
try {
if (child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.stop();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.child.stop"), e);
}
boolean destroy = false;
try {
if (!LifecycleState.DESTROYING.equals(child.getState())) {
child.destroy();
destroy = true;
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.child.destroy"), e);
}
if (!destroy) {
fireContainerEvent(REMOVE_CHILD_EVENT, child);
}
synchronized(children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) == null)
return;
children.remove(child.getName());
}
}Lifecycle的模板方法
- initInternal
startStopThreads 默认为 1 ,所以 reconfigureStartStopExecutor 方法会走 if 语句,而 startStopExecutor 最开始是没有赋值的,startStopExecutor instanceof InlineExecutorService 会返回 false,因此最终会执行 startStopExecutor = new InlineExecutorService(),InlineExecutorService 只是简单地实现了 java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService 类。 最终 reconfigureStartStopExecutor 给 startStopExecutor 这个成员变量设置了,startStopExecutor。
private int startStopThreads = 1;
protected ExecutorService startStopExecutor;
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
reconfigureStartStopExecutor(getStartStopThreads());
super.initInternal();
}
private void reconfigureStartStopExecutor(int threads) {
if (threads == 1) {
if (!(startStopExecutor instanceof InlineExecutorService)) {
startStopExecutor = new InlineExecutorService();
}
} else {
Server server = Container.getService(this).getServer();
server.setUtilityThreads(threads);
startStopExecutor = server.getUtilityExecutor();
}
}- startInternal
试想,container中有很多组件,而且属于Lifecycle生命周期管理;那么启动容器的时候,必然是逐个将这些子组件(包括子容器)启动起来。
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
logger = null;
getLogger();
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
if (backgroundProcessorDelay > 0) {
monitorFuture = Container.getService(ContainerBase.this).getServer()
.getUtilityExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
new ContainerBackgroundProcessorMonitor(), 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}- stopInternal
和initInternal初始化子组件方式倒过来,逐一停止子组件,并触发相关事件。
@Override
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (monitorFuture != null) {
monitorFuture.cancel(true);
monitorFuture = null;
}
threadStop();
setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING);
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle &&
((Lifecycle) pipeline).getState().isAvailable()) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).stop();
}
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StopChild(child)));
}
boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStopFailed"), e);
fail = true;
}
}
if (fail) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStopFailed"));
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).stop();
}
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).stop();
}
}- destroyInternal
对比下initInternal,它初始化了什么就destory什么
@Override
protected void destroyInternal() throws LifecycleException {
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).destroy();
}
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).destroy();
}
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).destroy();
}
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
removeChild(child);
}
if (parent != null) {
parent.removeChild(this);
}
if (startStopExecutor != null) {
startStopExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
super.destroyInternal();
}