上文我们学习了SpringAOP Cglib动态代理的实现,本文主要是SpringAOP JDK动态代理的案例和实现部分。@anarkh
- Spring进阶 - Spring AOP实现原理详解之JDK代理实现
- 引入
- 什么是JDK代理?
- JDK代理的案例
- 不需要maven依赖
- 定义实体
- 被代理的类和接口
- JDK代理类
- 使用代理
- 简单测试
- JDK代理的流程
- ProxyGenerator生成代码
- 从生成的Proxy代码看执行流程
- SpringAOP中JDK代理的实现
- SpringAOP Jdk代理的创建
- SpringAOP Jdk代理的执行
- 示例源码
引入
上文我们学习了SpringAOP Cglib动态代理的实现,本文主要是SpringAOP JDK动态代理的案例和实现部分。
什么是JDK代理?
JDK动态代理是有JDK提供的工具类Proxy实现的,动态代理类是在运行时生成指定接口的代理类,每个代理实例(实现需要代理的接口)都有一个关联的调用处理程序对象,此对象实现了InvocationHandler,最终的业务逻辑是在InvocationHandler实现类的invoke方法上。
JDK代理的案例
这里我们写一个使用jdk代理的简单例子。@anarkh
不需要maven依赖
jdk代理不需要任何依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>tech-anarkh-spring-demos</artifactId>
<groupId>tech.anarkh</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>006-spring-framework-demo-aop-proxy-jdk</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
</dependencies>
</project>定义实体
User
package tech.anarkh.springframework.entity;
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}被代理的类和接口
接口如下
package tech.anarkh.springframework.service;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface IUserService {
List<User> findUserList();
void addUser();
}实现类如下:
package tech.anarkh.springframework.service;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.entity.User;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
@Override
public List<User> findUserList() {
return Collections.singletonList(new User("anarkh", 18));
}
@Override
public void addUser() {
}
}JDK代理类
代理类如下:
package tech.anarkh.springframework.proxy;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.service.IUserService;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.service.UserServiceImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class UserLogProxy {
private IUserService target;
public UserLogProxy(UserServiceImpl target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
public IUserService getLoggingProxy() {
IUserService proxy;
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{IUserService.class};
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
System.out.println("[before] execute method: " + methodName);
Object result = null;
try {
result = method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("[after] execute method: " + methodName + ", return value: " + result);
return result;
}
};
proxy = (IUserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}使用代理
启动类中指定代理目标并执行。
package tech.anarkh.springframework;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.proxy.UserLogProxy;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.service.IUserService;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.service.UserServiceImpl;
public class ProxyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IUserService userService = new UserLogProxy(new UserServiceImpl()).getLoggingProxy();
userService.findUserList();
userService.addUser();
}
}简单测试
我们启动上述类main 函数,执行的结果如下:
[before] execute method: findUserList
[after] execute method: findUserList, return value: [User{name='anarkh', age=18}]
[before] execute method: addUser
[after] execute method: addUser, return value: nullJDK代理的流程
JDK代理自动生成的class是由sun.misc.ProxyGenerator来生成的。
ProxyGenerator生成代码
我们看下sun.misc.ProxyGenerator生成代码的逻辑:
public static byte[] generateProxyClass(final String name,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
int accessFlags)
{
ProxyGenerator gen = new ProxyGenerator(name, interfaces, accessFlags);
final byte[] classFile = gen.generateClassFile();
...
}generateClassFile方法如下:
private byte[] generateClassFile() {
addProxyMethod(hashCodeMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(equalsMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(toStringMethod, Object.class);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
for (Method m : intf.getMethods()) {
addProxyMethod(m, intf);
}
}
for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
checkReturnTypes(sigmethods);
}
try {
methods.add(generateConstructor());
for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
for (ProxyMethod pm : sigmethods) {
fields.add(new FieldInfo(pm.methodFieldName,
"Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;",
ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_STATIC));
methods.add(pm.generateMethod());
}
}
methods.add(generateStaticInitializer());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e);
}
if (methods.size() > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("method limit exceeded");
}
if (fields.size() > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("field limit exceeded");
}
cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className));
cp.getClass(superclassName);
for (Class<?> intf: interfaces) {
cp.getClass(dotToSlash(intf.getName()));
}
cp.setReadOnly();
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(bout);
try {
dout.writeInt(0xCAFEBABE);
dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MINOR_VERSION);
dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MAJOR_VERSION);
cp.write(dout);
dout.writeShort(accessFlags);
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className)));
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(superclassName));
dout.writeShort(interfaces.length);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(
dotToSlash(intf.getName())));
}
dout.writeShort(fields.size());
for (FieldInfo f : fields) {
f.write(dout);
}
dout.writeShort(methods.size());
for (MethodInfo m : methods) {
m.write(dout);
}
dout.writeShort(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e);
}
return bout.toByteArray();
}一共三个步骤(把大象装进冰箱分几步 ?):
- 第一步:(把冰箱门打开)准备工作,将所有方法包装成ProxyMethod对象,包括Object类中hashCode、equals、toString方法,以及被代理的接口中的方法
- 第二步:(把大象装进去)为代理类组装字段,构造函数,方法,static初始化块等
- 第三步:(把冰箱门带上)写入class文件
从生成的Proxy代码看执行流程
从上述sun.misc.ProxyGenerator类中可以看到,这个类里面有一个配置参数sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles,可以通过这个参数将生成的Proxy类保存在本地,比如设置为true 执行后,生成的文件如下:
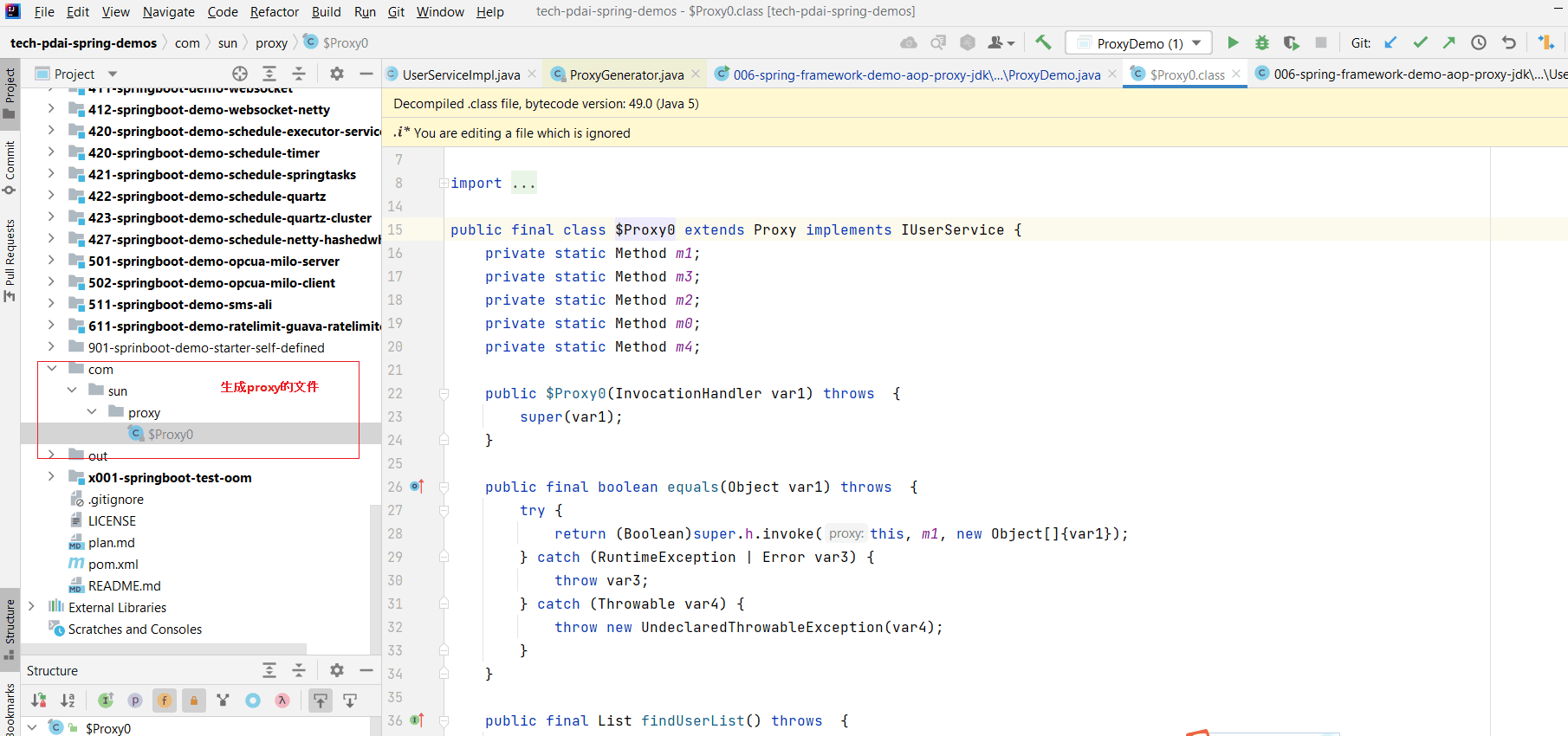
我们看下生成后的代码:
package com.sun.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
import java.util.List;
import tech.anarkh.springframework.service.IUserService;
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements IUserService {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m4;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws {
try {
return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1});
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {
throw var3;
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
}
}
public final List findUserList() throws {
try {
return (List)super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final String toString() throws {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final int hashCode() throws {
try {
return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final void addUser() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m3 = Class.forName("tech.anarkh.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("findUserList");
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
m4 = Class.forName("tech.anarkh.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("addUser");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}上述代码是比较容易理解的,我就不画图了。
主要流程是:
- ProxyGenerator创建Proxy的具体类$Proxy0
- 由static初始化块初始化接口方法:2个IUserService接口中的方法,3个Object中的接口方法
- 由构造函数注入InvocationHandler
- 执行的时候,通过ProxyGenerator创建的Proxy,调用InvocationHandler的invoke方法,执行我们自定义的invoke方法
SpringAOP中JDK代理的实现
SpringAOP扮演的是JDK代理的创建和调用两个角色,我们通过这两个方向来看下SpringAOP的代码(JdkDynamicAopProxy类)
SpringAOP Jdk代理的创建
代理的创建比较简单,调用getProxy方法,然后直接调用JDK中Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法将classloader和被代理的接口方法传入即可。
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);
}SpringAOP Jdk代理的执行
执行的方法如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}