本文主要对Collection - LinkedList进行源码解析。@anarkh
概述
LinkedList 同时实现了 List 接口和 Deque 接口,也就是说它既可以看作一个顺序容器,又可以看作一个队列(Queue),同时又可以看作一个栈(Stack)。这样看来, LinkedList 简直就是个全能冠军。当你需要使用栈或者队列时,可以考虑使用 LinkedList ,一方面是因为Java官方已经声明不建议使用 Stack 类,更遗憾的是,Java里根本没有一个叫做 Queue 的类(它是个接口名字)。关于栈或队列,现在的首选是 ArrayDeque ,它有着比 LinkedList(当作栈或队列使用时)有着更好的性能。
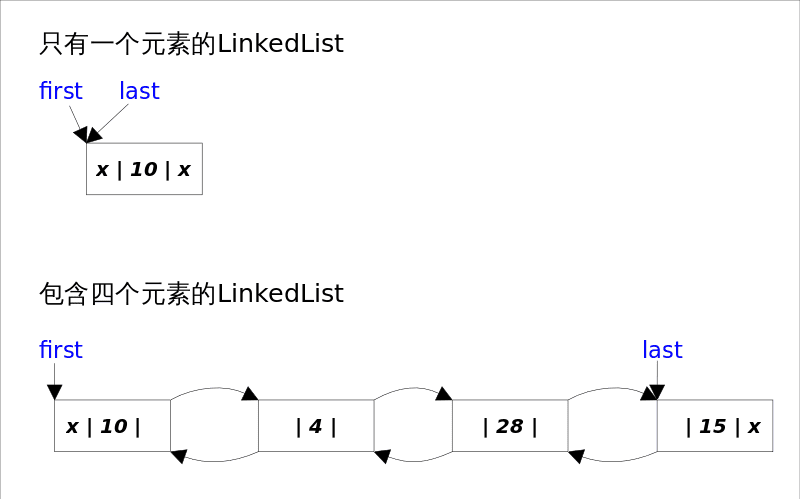
LinkedList 的实现方式决定了所有跟下标相关的操作都是线性时间,而在首段或者末尾删除元素只需要常数时间。为追求效率 LinkedList 没有实现同步(synchronized),如果需要多个线程并发访问,可以先采用Collections.synchronizedList()方法对其进行包装。
LinkedList实现
底层数据结构
LinkedList 底层通过双向链表实现 ,本节将着重讲解插入和删除元素时双向链表的维护过程,也即是之间解跟 List 接口相关的函数,而将 Queue 和 Stack 以及 Deque 相关的知识放在下一节讲。双向链表的每个节点用内部类 Node 表示。 LinkedList 通过first和last引用分别指向链表的第一个和最后一个元素。注意这里没有所谓的哑元,当链表为空的时候first和last都指向null。
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;其中Node是私有的内部类:
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}getFirst(), getLast()
获取第一个元素, 和获取最后一个元素:
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}removeFirst(), removeLast(), remove(e), remove(index)
remove()方法也有两个版本,一个是删除跟指定元素相等的第一个元素remove(Object o),另一个是删除指定下标处的元素remove(int index)。
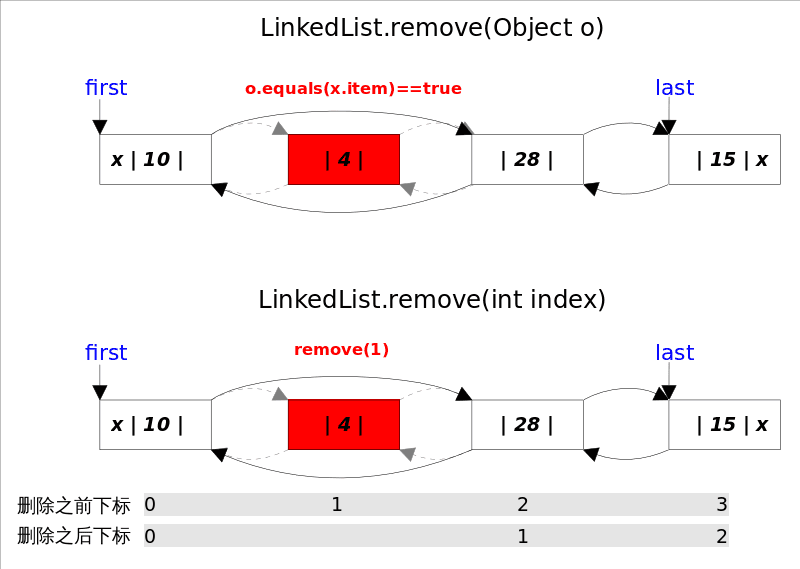
删除元素 - 指的是删除第一次出现的这个元素, 如果没有这个元素,则返回false;判断的依据是equals方法, 如果equals,则直接unlink这个node;由于LinkedList可存放null元素,故也可以删除第一次出现null的元素;
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}remove(int index)使用的是下标计数, 只需要判断该index是否有元素即可,如果有则直接unlink这个node。
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}删除head元素:
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null;
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}删除last元素:
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null;
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}add()
_add()_方法有两个版本,一个是add(E e),该方法在_LinkedList_的末尾插入元素,因为有last指向链表末尾,在末尾插入元素的花费是常数时间。只需要简单修改几个相关引用即可;另一个是add(int index, E element),该方法是在指定下表处插入元素,需要先通过线性查找找到具体位置,然后修改相关引用完成插入操作。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}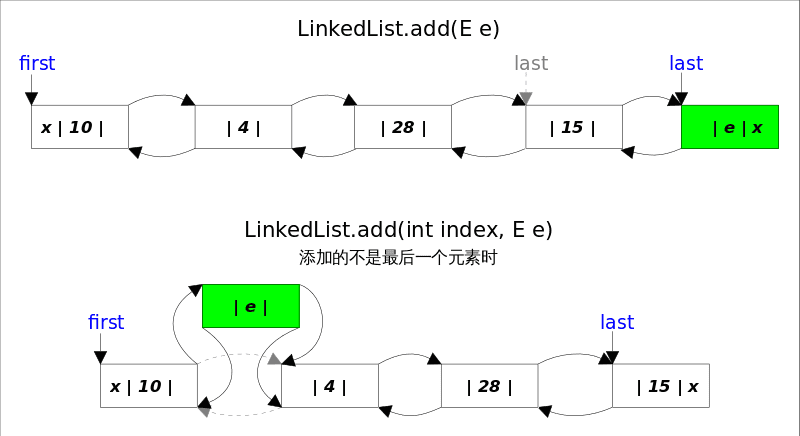
add(int index, E element), 当index==size时,等同于add(E e); 如果不是,则分两步: 1.先根据index找到要插入的位置,即node(index)方法;2.修改引用,完成插入操作。
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}上面代码中的node(int index)函数有一点小小的trick,因为链表双向的,可以从开始往后找,也可以从结尾往前找,具体朝那个方向找取决于条件index < (size >> 1),也即是index是靠近前端还是后端。从这里也可以看出,linkedList通过index检索元素的效率没有arrayList高。
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}addAll()
addAll(index, c) 实现方式并不是直接调用add(index,e)来实现,主要是因为效率的问题,另一个是fail-fast中modCount只会增加1次;
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}clear()
为了让GC更快可以回收放置的元素,需要将node之间的引用关系赋空。
public void clear() {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}Positional Access 方法
通过index获取元素
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}将某个位置的元素重新赋值:
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}将元素插入到指定index位置:
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}删除指定位置的元素:
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}其它位置的方法:
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}查找操作
查找操作的本质是查找元素的下标:
查找第一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}查找最后一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}Queue 方法
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}Deque 方法
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}参考
- Java LinkedList源码剖析 结合源码对LinkedList进行讲解 http://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/5457150.html