本文主要从JDK 11源码角度分析 OutputStream。 @anarkh
OutputStream 类实现关系
OutputStream是输出字节流,具体的实现类层次结构如下:
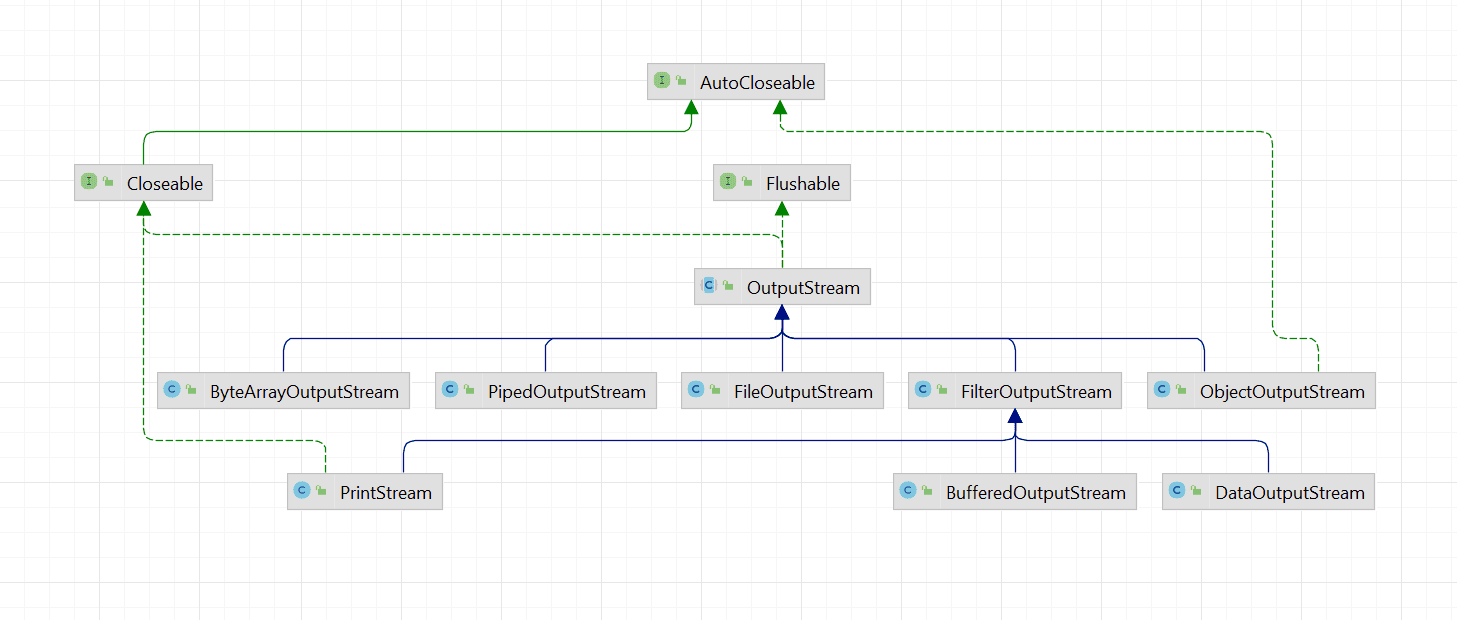
OutputStream 抽象类
OutputStream 类重要方法设计如下:
java
public abstract void write(int b)
public void write(byte b[])
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len)
public void flush()
public void close()源码实现
梳理部分OutputStream及其实现类的源码分析。
OutputStream
OutputStream抽象类源码如下:
java
public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable, Flushable {
public static OutputStream nullOutputStream() {
return new OutputStream() {
private volatile boolean closed;
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (closed) {
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
}
@Override
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
ensureOpen();
}
@Override
public void close() {
closed = true;
}
};
}
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
write(b[off + i]);
}
}
public void flush() throws IOException {
}
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}补充下JDK11为什么会增加nullOutputStream方法的设计?即空对象模式
- 空对象模式
举个例子:
java
public class MyParser implements Parser {
private static Action NO_ACTION = new Action() {
public void doSomething() { }
};
public Action findAction(String userInput) {
if ( ) {
return NO_ACTION;
}
}
}然后便可以始终可以这么调用,而不用再判断空了
java
ParserFactory.getParser().findAction(someInput).doSomething();FilterOutputStream
FilterOutputStream 源码如下
java
public class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream {
protected OutputStream out;
private volatile boolean closed;
private final Object closeLock = new Object();
public FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this.out = out;
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
out.write(b);
}
@Override
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
@Override
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if ((off | len | (b.length - (len + off)) | (off + len)) < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
write(b[off + i]);
}
}
@Override
public void flush() throws IOException {
out.flush();
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
if (closed) {
return;
}
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed) {
return;
}
closed = true;
}
Throwable flushException = null;
try {
flush();
} catch (Throwable e) {
flushException = e;
throw e;
} finally {
if (flushException == null) {
out.close();
} else {
try {
out.close();
} catch (Throwable closeException) {
if ((flushException instanceof ThreadDeath) &&
!(closeException instanceof ThreadDeath)) {
flushException.addSuppressed(closeException);
throw (ThreadDeath) flushException;
}
if (flushException != closeException) {
closeException.addSuppressed(flushException);
}
throw closeException;
}
}
}
}
}@anarkh: 对比下JDK8中,close方法是没有加锁处理的。这种情况下你可以看JDK8源码中,直接利用java7的try with resources方式,优雅的调用flush方法后对out进行关闭。
java
public void close() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream ostream = out) {
flush();
}
}ByteArrayOutputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream 源码如下
java
public class ByteArrayOutputStream extends OutputStream {
protected byte buf[];
protected int count;
public ByteArrayOutputStream() {
this(32);
}
public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size) {
if (size < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative initial size: "
+ size);
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity - buf.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = buf.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
public synchronized void write(int b) {
ensureCapacity(count + 1);
buf[count] = (byte) b;
count += 1;
}
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
ensureCapacity(count + len);
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
count += len;
}
public void writeBytes(byte b[]) {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
public synchronized void writeTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(buf, 0, count);
}
public synchronized void reset() {
count = 0;
}
public synchronized byte[] toByteArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(buf, count);
}
public synchronized int size() {
return count;
}
public synchronized String toString() {
return new String(buf, 0, count);
}
public synchronized String toString(String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
{
return new String(buf, 0, count, charsetName);
}
public synchronized String toString(Charset charset) {
return new String(buf, 0, count, charset);
}
@Deprecated
public synchronized String toString(int hibyte) {
return new String(buf, hibyte, 0, count);
}
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}BufferedOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream 源码如下
java
public class BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream {
protected byte buf[];
protected int count;
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {
super(out);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
if (count > 0) {
out.write(buf, 0, count);
count = 0;
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException {
if (count >= buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
}
buf[count++] = (byte)b;
}
@Override
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (len >= buf.length) {
flushBuffer();
out.write(b, off, len);
return;
}
if (len > buf.length - count) {
flushBuffer();
}
System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);
count += len;
}
@Override
public synchronized void flush() throws IOException {
flushBuffer();
out.flush();
}
}参考文章
- JDK 11