本文主要从JDK 11 源码 角度分析InputStream。 @anarkh
InputStream 类实现关系
InputStream是输入字节流,具体的实现类层次结构如下:
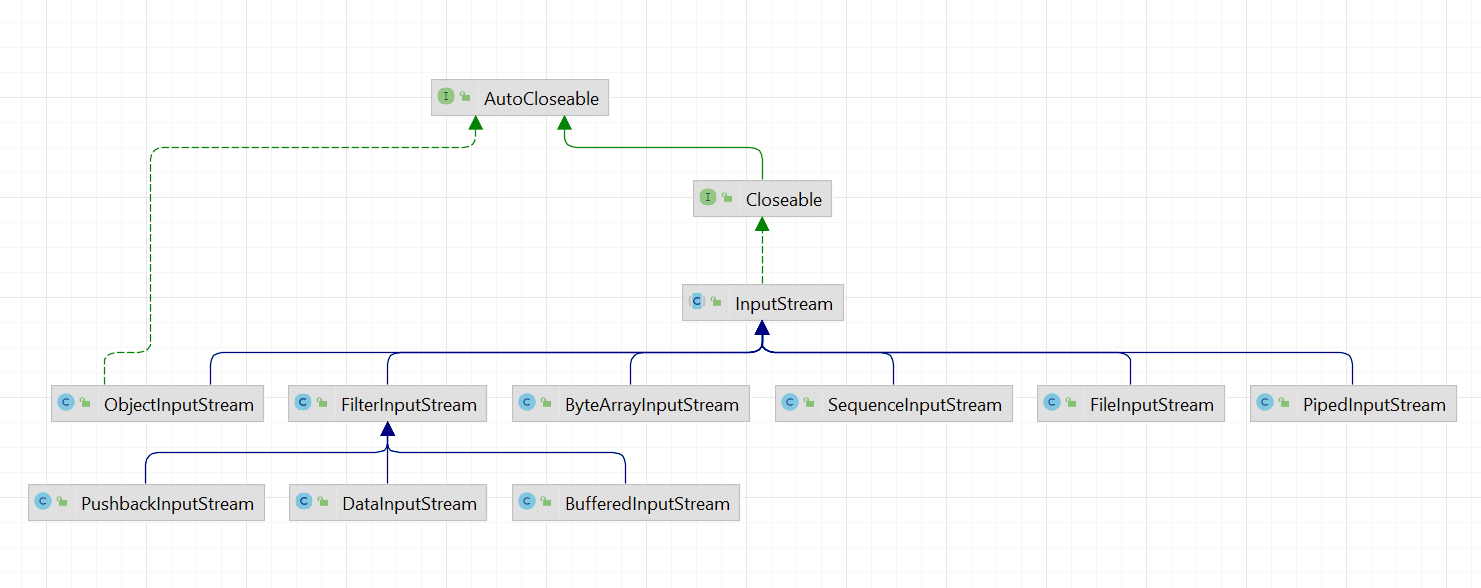
InputStream 抽象类
InputStream 类重要方法设计如下:
java
public abstract int read()
public int read(byte b[])
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
public byte[] readAllBytes()
public byte[] readNBytes(int len)
public int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len)
public long skip(long n)
public int available()
public void close()
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit)
public synchronized void reset()
public boolean markSupported()
public long transferTo(OutputStream out)源码实现
梳理部分InputStream及其实现类的源码分析。
InputStream
InputStream抽象类源码如下:
java
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;
private static final int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
public static InputStream nullInputStream() {
return new InputStream() {
private volatile boolean closed;
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (closed) {
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
}
@Override
public int available () throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
return 0;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
return -1;
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
ensureOpen();
return -1;
}
@Override
public byte[] readAllBytes() throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
return new byte[0];
}
@Override
public int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len)
throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
ensureOpen();
return 0;
}
@Override
public byte[] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException {
if (len < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("len < 0");
}
ensureOpen();
return new byte[0];
}
@Override
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
return 0L;
}
@Override
public long transferTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
Objects.requireNonNull(out);
ensureOpen();
return 0L;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
closed = true;
}
};
}
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int c = read();
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte)c;
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
private static final int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
public byte[] readAllBytes() throws IOException {
return readNBytes(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public byte[] readNBytes(int len) throws IOException {
if (len < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("len < 0");
}
List<byte[]> bufs = null;
byte[] result = null;
int total = 0;
int remaining = len;
int n;
do {
byte[] buf = new byte[Math.min(remaining, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)];
int nread = 0;
while ((n = read(buf, nread,
Math.min(buf.length - nread, remaining))) > 0) {
nread += n;
remaining -= n;
}
if (nread > 0) {
if (MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - total < nread) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
}
total += nread;
if (result == null) {
result = buf;
} else {
if (bufs == null) {
bufs = new ArrayList<>();
bufs.add(result);
}
bufs.add(buf);
}
}
} while (n >= 0 && remaining > 0);
if (bufs == null) {
if (result == null) {
return new byte[0];
}
return result.length == total ?
result : Arrays.copyOf(result, total);
}
result = new byte[total];
int offset = 0;
remaining = total;
for (byte[] b : bufs) {
int count = Math.min(b.length, remaining);
System.arraycopy(b, 0, result, offset, count);
offset += count;
remaining -= count;
}
return result;
}
public int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
int n = 0;
while (n < len) {
int count = read(b, off + n, len - n);
if (count < 0)
break;
n += count;
}
return n;
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
long remaining = n;
int nr;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int size = (int)Math.min(MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining);
byte[] skipBuffer = new byte[size];
while (remaining > 0) {
nr = read(skipBuffer, 0, (int)Math.min(size, remaining));
if (nr < 0) {
break;
}
remaining -= nr;
}
return n - remaining;
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return 0;
}
public void close() throws IOException {}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported");
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
public long transferTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
Objects.requireNonNull(out, "out");
long transferred = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE];
int read;
while ((read = this.read(buffer, 0, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)) >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, read);
transferred += read;
}
return transferred;
}总结下JDK9的更新点
类 java.io.InputStream 中增加了新的方法来读取和复制 InputStream 中包含的数据。
readAllBytes:读取 InputStream 中的所有剩余字节。readNBytes: 从 InputStream 中读取指定数量的字节到数组中。transferTo:读取 InputStream 中的全部字节并写入到指定的 OutputStream 中 。
java
public class TestInputStream {
private InputStream inputStream;
private static final String CONTENT = "Hello World";
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
this.inputStream =
TestInputStream.class.getResourceAsStream("/input.txt");
}
@Test
public void testReadAllBytes() throws Exception {
final String content = new String(this.inputStream.readAllBytes());
assertEquals(CONTENT, content);
}
@Test
public void testReadNBytes() throws Exception {
final byte[] data = new byte[5];
this.inputStream.readNBytes(data, 0, 5);
assertEquals("Hello", new String(data));
}
@Test
public void testTransferTo() throws Exception {
final ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
this.inputStream.transferTo(outputStream);
assertEquals(CONTENT, outputStream.toString());
}
}read(byte[], int, int)和readNBytes(byte[], int, int)看似是实现的相同功能,为何会设计readNBytes方法呢?
这个问题可以参看这里在新窗口打开
- read(byte[], int, int)是尝试读到最多len个bytes,但是读取到的内容长度可能是小于len 的。
- readNBytes(byte[], int, int) 会一直(while循环)查找直到stream尾为止
举个例子:如果文本内容是12345<end>, read(s,0,10)是允许返回123的, 而readNbytes(s,0,10)会一直(while循环)查找直到stream尾为止,并返回12345.
补充下JDK11为什么会增加nullInputStream方法的设计?即空对象模式
- 空对象模式
举个例子:
java
public class MyParser implements Parser {
private static Action NO_ACTION = new Action() {
public void doSomething() { }
};
public Action findAction(String userInput) {
if ( ) {
return NO_ACTION;
}
}
}然后便可以始终可以这么调用,而不用再判断空了
java
ParserFactory.getParser().findAction(someInput).doSomething();FilterInputStream
FilterInputStream 源码如下
java
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in;
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return in.read(b, off, len);
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
return in.skip(n);
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return in.available();
}
public void close() throws IOException {
in.close();
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
in.mark(readlimit);
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
in.reset();
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return in.markSupported();
}
}为什么被装饰的inputStream是volatile类型的 ?
请参看: 关键字: volatile详解
ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayInputStream源码如下
java
public class ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream {
protected byte buf[];
protected int pos;
protected int mark = 0;
protected int count;
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[]) {
this.buf = buf;
this.pos = 0;
this.count = buf.length;
}
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) {
this.buf = buf;
this.pos = offset;
this.count = Math.min(offset + length, buf.length);
this.mark = offset;
}
public synchronized int read() {
return (pos < count) ? (buf[pos++] & 0xff) : -1;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (pos >= count) {
return -1;
}
int avail = count - pos;
if (len > avail) {
len = avail;
}
if (len <= 0) {
return 0;
}
System.arraycopy(buf, pos, b, off, len);
pos += len;
return len;
}
public synchronized long skip(long n) {
long k = count - pos;
if (n < k) {
k = n < 0 ? 0 : n;
}
pos += k;
return k;
}
public synchronized int available() {
return count - pos;
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) {
mark = pos;
}
public synchronized void reset() {
pos = mark;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
}
}BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream源码如下
java
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
protected volatile byte buf[];
private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte[]> bufUpdater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf");
protected int count;
protected int pos;
protected int markpos = -1;
protected int marklimit;
private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException {
InputStream input = in;
if (input == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return input;
}
private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = buf;
if (buffer == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return buffer;
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0;
else if (pos >= buffer.length)
if (markpos > 0) {
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1;
pos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
} else {
int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ?
pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
int avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) {
if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) {
return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);
}
fill();
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) return -1;
}
int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len;
System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt);
pos += cnt;
return cnt;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
throws IOException
{
getBufIfOpen();
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
if (nread <= 0)
return (n == 0) ? nread : n;
n += nread;
if (n >= len)
return n;
InputStream input = in;
if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)
return n;
}
}
public synchronized long skip(long n) throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen();
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
long avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) {
if (markpos <0)
return getInIfOpen().skip(n);
fill();
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0)
return 0;
}
long skipped = (avail < n) ? avail : n;
pos += skipped;
return skipped;
}
public synchronized int available() throws IOException {
int n = count - pos;
int avail = getInIfOpen().available();
return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail)
? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: n + avail;
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
marklimit = readlimit;
markpos = pos;
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
throw new IOException("Resetting to invalid mark");
pos = markpos;
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer;
while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {
if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) {
InputStream input = in;
in = null;
if (input != null)
input.close();
return;
}
}
}
}AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater具体可以参考:JUC原子类: CAS, Unsafe和原子类详解